KNX: The Global Standard for Smart Home and Building Automation
In today’s era of smart homes and intelligent buildings, seamless automation and device integration are no longer luxury—they are essential. KNX stands as the world’s leading open standard for home and building control, enabling professionals and enthusiasts to create robust, flexible, and future-proof automation systems.
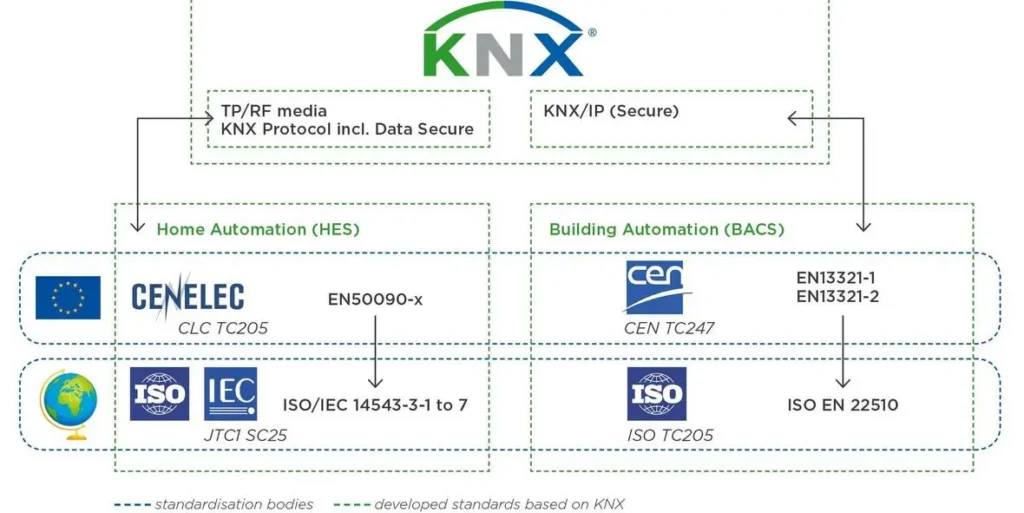
What is KNX?
KNX is a globally recognized communication protocol for home and building automation. It allows devices from different manufacturers—such as lighting, HVAC, security systems, and audio/video equipment—to communicate and work together seamlessly over a single network.
Key points about KNX:
- Open Standard:Vendor-independent, no lock-in to a single manufacturer.
- Global Adoption:Used in over 190 countries with tens of thousands of certified products.
- Reliable & Scalable:From a single apartment to large commercial buildings.
- Flexible Communication:Supports twisted pair (TP), powerline (PL), radio frequency (RF), and IP/Ethernet.
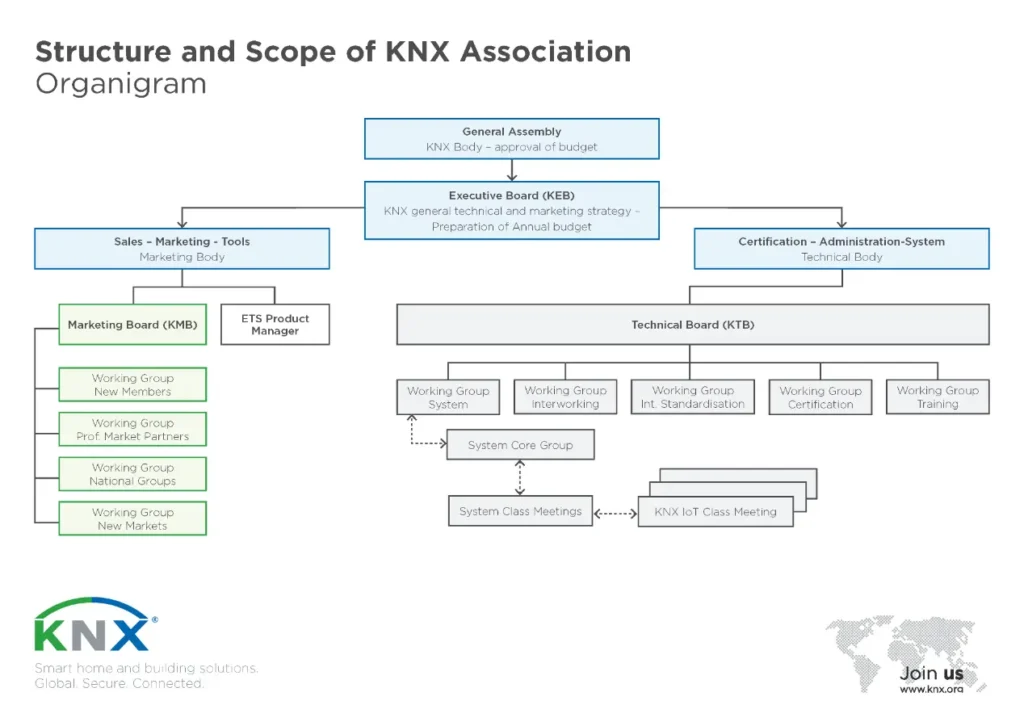
History and Development of KNX
- 1990s:KNX emerged from a merger of three European standards: EIB (European Installation Bus), EHS (European Home Systems), and BATIBUS.
- 2002:KNX Association officially formed to manage certification, standardization, and promotion.
- 2006:KNX became an ISO/IEC 14543-3 standard, solidifying its global recognition.
- Today:KNX continues to evolve with KNX IoT and KNX over IP, supporting integration with cloud services, voice assistants, and advanced smart home systems.
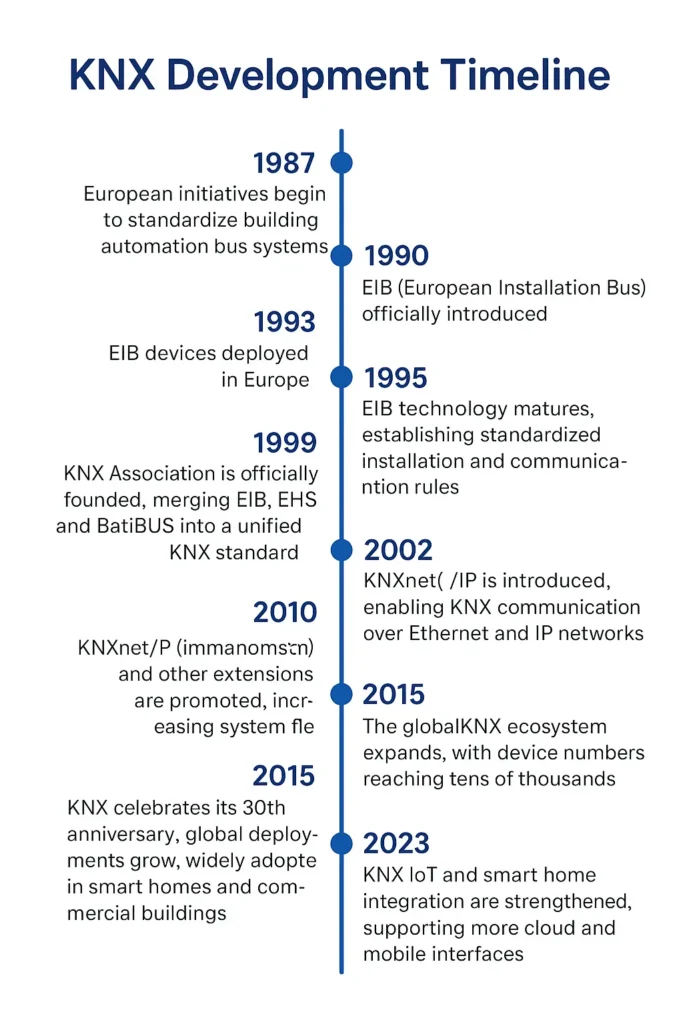
KNX Development Timeline
- 1987: European initiatives begin to standardize building automation bus systems.
- 1990: The predecessor of KNX—EIB (European Installation Bus)—is officially introduced.
- 1993: EIB devices and applications start to be deployed in the European market.
- 1995: EIB technology matures, establishing standardized installation and communication rules.
- 1999: KNX Association is officially founded, merging EIB, EHS (European Home Systems), and BatiBUS into a unified KNX standard.
- 2002: KNX is adopted as an international standard by ISO/IEC 14543-3.
- 2006: KNXnet/IP is introduced, enabling KNX communication over Ethernet and IP networks.
- 2010: KNX RF (wireless communication) and other extensions are promoted, increasing system flexibility.
- 2015: The global KNX ecosystem expands, with device numbers reaching tens of thousands.
- 2020: KNX celebrates its 30th anniversary; global deployments grow, widely adopted in smart homes and commercial buildings.
- 2023: KNX IoT and smart home integration are strengthened, supporting more cloud and mobile interfaces.
- 2025: KNX celebrates its 35th anniversary; over 10,000 compatible devices worldwide, maintaining its position as a leading global building automation standard.
Major Participants:
- Siemens, Schneider Electric, ABB, Hager, Gira, Jung, Legrand– Key manufacturers contributing to devices, modules, and KNX-certified solutions.
- KNX Association– Oversees standardization, certification, and education worldwide.
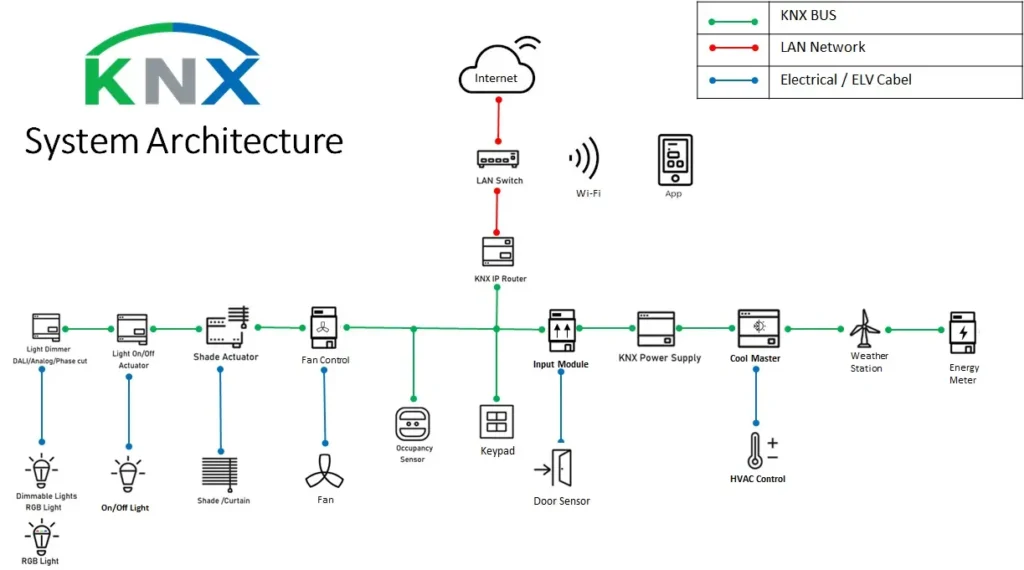
KNX Protocol: How Devices Communicate
1.Physical Layers (Transmission Media)
| KNX Medium | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Twisted Pair (KNX TP1) | Dedicated two-wire bus for control signals | Homes, offices |
| Powerline (KNX PL) | Signals over mains wiring | Retrofitting older buildings |
| Radio Frequency (KNX RF) | Wireless communication | Devices without wiring |
| Ethernet / IP (KNXnet/IP) | IP-based tunneling or routing | Integration with IT networks, cloud, or multi-site setups |
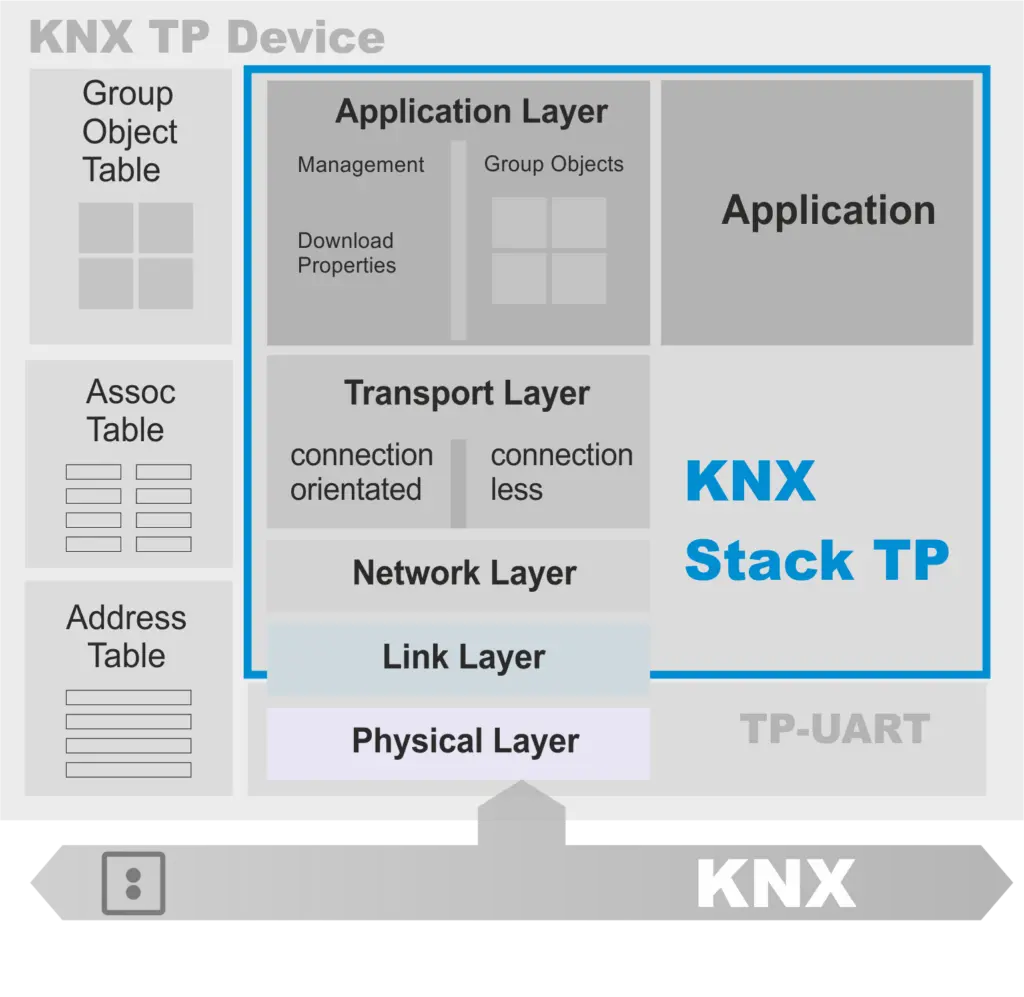
2.KNX Protocol Stack
KNX uses a layered architecture similar to OSI:
- Physical Layer– Transmits signals over TP, PL, RF, or IP.
- Data Link Layer– Detects errors, handles bus arbitration.
- Network Layer– Routes messages across lines and areas.
- Transport Layer– Ensures reliable delivery.
- Application Layer– Standardizes device functions; e.g., a light switch can control any KNX-certified lamp.
3.KNX Addresses and Communication Types
- Physical Address:Unique device ID (e.g., 1.1.5)
- Group Address:Logical address for controlling functions (e.g., all lights in a room)
- Communication Types:Broadcast, Multicast (group), Unicast
This addressing system allows precise control of multi-room setups, such as adjusting volume in one zone while keeping others independent.
4.KNX Application Protocols
- Lighting Control:Switch, dim, scene management
- Climate Control:HVAC, temperature sensors, thermostats
- Security:Motion sensors, alarms, door contacts
- Audio/Video:Multi-room streaming, AV routing, volume, mute, and zone control
Standardized Data Point Types (DPTs) ensure devices from different brands understand the same commands.
5.KNX Advantages Over Proprietary Protocols
- Vendor Independence:Mix devices from different manufacturers.
- Longevity:Certified devices remain compatible for decades.
- Interoperability:Any certified KNX device integrates seamlessly.
- Flexibility:Supports both wired and wireless deployment.
- Energy Efficiency:Coordinated control reduces electricity consumption.
KNX in Multi-Room Audio
KNX is increasingly popular for multi-room streaming amplifiers, offering:
- Volume, Mute, Source, and Routing Controlfrom KNX wall panels.
- Integration with devices like AmpVortex-16060or AmpVortex-16100 via:
- 1Home Server KNX Pro
- KNX IP Interface
- AmpVortex KNX Module
- Built-in KNX Amplifiers
- Automated music scheduling, integration with lighting, climate, and security.
Conclusion
KNX is more than a protocol; it’s the backbone of modern smart homes and intelligent buildings. It provides:
- Reliable interoperability across brands
- Scalable systems from single apartments to large buildings
- Future-proof and flexible integration
- Optimized energy usage
For homeowners, integrators, and AV professionals, KNX guarantees robust, seamless, and long-lasting smart home automation, including full integration with multi-room audio systems.
To learn more about multi-room streaming amplifiers, home automation, KNX integration, and audio technologies, visit www.ampvortex.com.
